Implement Stack using Queues
We are given a Queue data structure that supports standard operations like enqueue() and dequeue(). We need to implement a Stack data structure using only instances of Queue and queue operations allowed on the instances
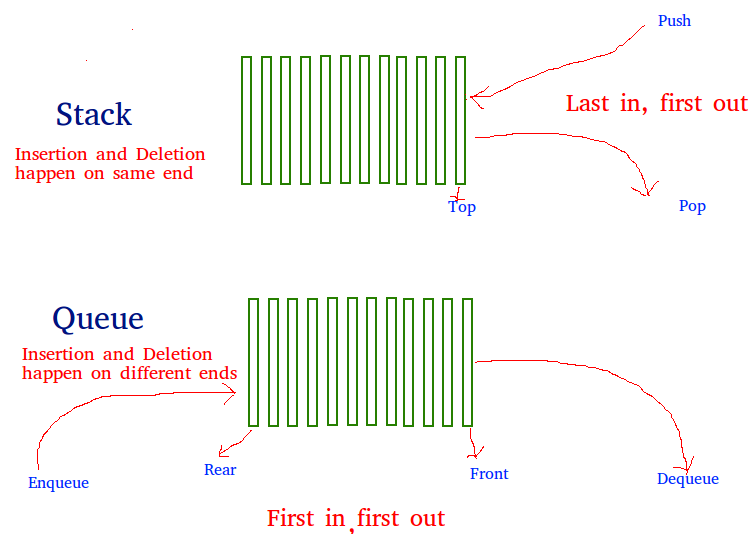
A stack can be implemented using two queues. Let stack to be implemented be ‘s’ and queues used to implement be ‘q1’ and ‘q2’. Stack ‘s’ can be implemented in two ways:
Method 1 (By making push operation costly)
This method makes sure that newly entered element is always at the front of ‘q1’, so that pop operation just dequeues from ‘q1’. ‘q2’ is used to put every new element at front of ‘q1’.
- push(s, x) operation’s step are described below:
- Enqueue x to q2
- One by one dequeue everything from q1 and enqueue to q2.
- Swap the names of q1 and q2
- pop(s) operation’s function are described below:
- Dequeue an item from q1 and return it.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
/* Java Program to implement a stack using two queue */import java.util.*; class GfG { static class Stack { // Two inbuilt queues static Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); static Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<Integer>(); // To maintain current number of // elements static int curr_size; Stack() { curr_size = 0; } static void push(int x) { curr_size++; // Push x first in empty q2 q2.add(x); // Push all the remaining // elements in q1 to q2. while (!q1.isEmpty()) { q2.add(q1.peek()); q1.remove(); } // swap the names of two queues Queue<Integer> q = q1; q1 = q2; q2 = q; } static void pop() { // if no elements are there in q1 if (q1.isEmpty()) return; q1.remove(); curr_size--; } static int top() { if (q1.isEmpty()) return -1; return q1.peek(); } static int size() { return curr_size; } } // driver code public static void main(String[] args) { Stack s = new Stack(); s.push(1); s.push(2); s.push(3); System.out.println("current size: " + s.size()); System.out.println(s.top()); s.pop(); System.out.println(s.top()); s.pop(); System.out.println(s.top()); System.out.println("current size: " + s.size()); }}// This code is contributed by Prerna |
Output :
current size: 3321current size: 1
Way 2 (By making pop operation costly)
In push operation, the new element is always enqueued to q1. In pop() operation, if q2 is empty then all the elements except the last, are moved to q2. Finally the last element is dequeued from q1 and returned.
- push(s, x) operation:
- Enqueue x to q1 (assuming size of q1 is unlimited).
- pop(s) operation:
- One by one dequeue everything except the last element from q1 and enqueue to q2.
- Dequeue the last item of q1, the dequeued item is result, store it.
- Swap the names of q1 and q2
- Return the item stored in step 2.
usingSystem;usingSystem.Collections;classGfG{publicclassStack{publicQueue q1 =newQueue();publicQueue q2 =newQueue();//Just enqueue the new element to q1publicvoidPush(intx) => q1.Enqueue(x);//move all elements from q1 to q2 except the rear of q1.//Store the rear of q1//swap q1 and q2//return the stored resultpublicintPop(){if(q1.Count == 0)return-1;while(q1.Count > 1){q2.Enqueue(q1.Dequeue());}intres = (int)q1.Dequeue();Queue temp = q1;q1 = q2;q2 = temp;returnres;}publicintSize() => q1.Count;publicintTop(){if(q1.Count == 0)return-1;while(q1.Count > 1){q2.Enqueue(q1.Dequeue());}intres = (int)q1.Dequeue();q2.Enqueue(res);Queue temp = q1;q1 = q2;q2 = temp;returnres;}};publicstaticvoidMain(String[] args){Stack s =newStack();s.Push(1);Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: "+ s.Size() +"\tTop : "+ s.Top());s.Push(7);Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: "+ s.Size() +"\tTop : "+ s.Top());s.Push(9);Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: "+ s.Size() +"\tTop : "+ s.Top());s.Pop();Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: "+ s.Size() +"\tTop : "+ s.Top());s.Pop();Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: "+ s.Size() +"\tTop : "+ s.Top());s.Push(5);Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: "+ s.Size() +"\tTop : "+ s.Top());}}//Submitted by Sakti Prasad//Size of Stack: 1 Top : 1//Size of Stack: 2 Top : 7//Size of Stack: 3 Top : 9//Size of Stack: 2 Top : 7//Size of Stack: 1 Top : 1//Size of Stack: 2 Top : 5Output :
current size: 4432current size: