Chain Of Responsibility Pattern
Chain Of Responsibility Pattern
In chain of responsibility, sender sends a request to a chain of objects. The request can be handled by any object in the chain.
A Chain of Responsibility Pattern says that just “avoid coupling the sender of a request to its receiver by giving multiple objects a chance to handle the request”. For example, an ATM uses the Chain of Responsibility design pattern in money giving process.
In other words, we can say that normally each receiver contains reference of another receiver. If one object cannot handle the request then it passes the same to the next receiver and so on.
Advantage of Chain of Responsibility Pattern
- It reduces the coupling.
- It adds flexibility while assigning the responsibilities to objects.
- It allows a set of classes to act as one; events produced in one class can be sent to other handler classes with the help of composition.
Usage of Chain of Responsibility Pattern:
It is used:
- When more than one object can handle a request and the handler is unknown.
- When the group of objects that can handle the request must be specified in dynamic way.
Example of Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Let’s understand the example of Chain of Responsibility Pattern by the above UML diagram.
UML for Chain of Responsibility Pattern:
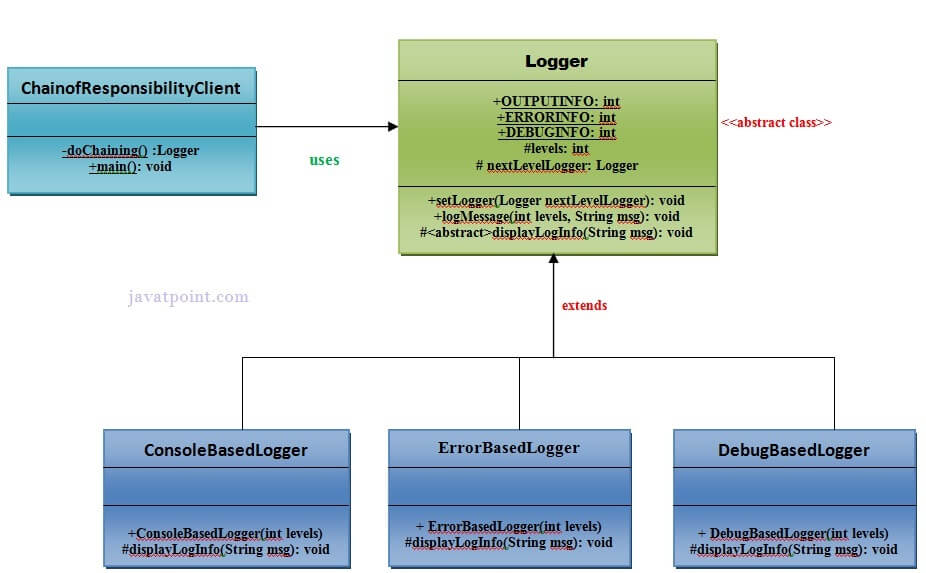
Implementation of above UML:
Step 1
Create a Logger abstract class.
public abstract class Logger {
public static int OUTPUTINFO = 1;
public static int ERRORINFO = 2;
public static int DEBUGINFO = 3;
protected int levels;
protected Logger nextLevelLogger;
public void setNextLevelLogger(Logger nextLevelLogger) {
this.nextLevelLogger = nextLevelLogger;
}
public void logMessage(int levels, String msg) {
if(this.levels <= levels) {
displayLogInfo(msg);
}
if (nextLevelLogger != null) {
nextLevelLogger.logMessage(levels, msg);
}
}
protected abstract void displayLogInfo(String msg);
}
Step 2
Create a ConsoleBasedLogger class.
public class ConsoleBasedLogger extends Logger {
public ConsoleBasedLogger(int levels) {
this.levels = levels;
}
@Override
protected void displayLogInfo(String msg) {
System.out.println(“CONSOLE LOGGER INFO: ” + msg);
}
}
Step 3
Create a DebugBasedLogger class.
public class DebugBasedLogger extends Logger {
public DebugBasedLogger(int levels) {
this.levels = levels;
}
@Override
protected void displayLogInfo(String msg) {
System.out.println(“DEBUG LOGGER INFO: ” + msg);
}
}// End of the DebugBasedLogger class.
Step 4
Create a ErrorBasedLogger class.
public class ErrorBasedLogger extends Logger {
public ErrorBasedLogger(int levels) {
this.levels = levels;
}
@Override
protected void displayLogInfo(String msg) {
System.out.println(“ERROR LOGGER INFO: ” + msg);
}
}// End of the ErrorBasedLogger class.
Step 5
Create a ChainOfResponsibilityClient class.
public class ChainofResponsibilityClient {
private static Logger doChaining() {
Logger consoleLogger = new ConsoleBasedLogger(Logger.OUTPUTINFO);
Logger errorLogger = new ErrorBasedLogger(Logger.ERRORINFO);
consoleLogger.setNextLevelLogger(errorLogger);
Logger debugLogger = new DebugBasedLogger(Logger.DEBUGINFO);
errorLogger.setNextLevelLogger(debugLogger);
return consoleLogger;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Logger chainLogger = doChaining();
chainLogger.logMessage(Logger.OUTPUTINFO, “Enter the sequence of values “);
chainLogger.logMessage(Logger.ERRORINFO, “An error is occured now”);
chainLogger.logMessage(Logger.DEBUGINFO, “This was the error now debugging is compeled”);
}
}
Output:
bilityClient
CONSOLE LOGGER INFO: Enter the sequence of values
CONSOLE LOGGER INFO: An error is occured now
ERROR LOGGER INFO: An error is occured now
CONSOLE LOGGER INFO: This was the error now debugging is compeled
ERROR LOGGER INFO: This was the error now debugging is compeled
DEBUG LOGGER INFO: This was the error now debugging is compeled